Institute of Bioinformatics Münster
DOGMA
Validation of Genome Annotation with Conserved Protein Domains and Domain Arrangements
Summary
| Species | Description [%] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDA Size | Total | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| P. californicus | 97.12 | 95.59 | 94.34 | 96.31 |
| P. barbatus | 98.24 | 97.83 | 97.45 | 98.02 |
| S. invicta | 98.80 | 96.91 | 93.98 | 97.64 |
| C. floridanus | 98.92 | 99.08 | 98.54 | 98.92 |
| A. mellifera | 98.35 | 98.68 | 98.18 | 98.44 |
Description
DOGMA is a quality assessment tool for predicting conserved domain arrangements (CDA) in proteome and transcriptome data. It uses a database consisting of CDAs which are specific for different clades, such as eukaryotes or insects. It is checking how many of the CDAs are mapping and how many where expected to map to the proteome or transcriptome. So, it gives a clue of the completeness of the proteome or transcriptome based on the amount of mapping CDAs.
Results
The insect database holds 2,673 single-domain CDAs and 2,068 multiple-domain CDAs. DOGMA found 96.31% (4,566 of 4,741 conserved domains) of the conserved domain arrangements from insects in the final protein predictions of MAKER.
Download DOGMA output file:DOGMA insect validation
Discussion
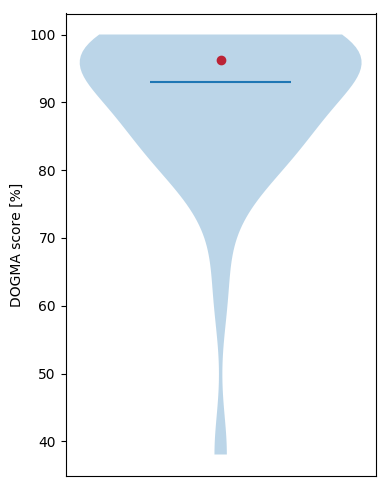
- Figure 1: Distribution of DOGMA scores within the insect database (red point = P. californicus score, blue bar = average of DOGMA scores from validated insects).
References
- Elias Dohmen, Lukas P.M. Kremer, Erich Bornberg-Bauer, Carsten Kemena; DOGMA: domain-based transcriptome and proteome quality assessment, Bioinformatics, Volume 32, Issue 17, 1 September 2016, Pages 2577–2581, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw231
2020-11-18 22:19