Institute of Bioinformatics Münster
Functional predictions
Functional annotation of MAKER predictions
It is recommended to use any other browser besides Firefox for opening this webpage.
Summary
This section includes functional classification as identification of sequence similarity to proteins from P. californicus.| Functional classification | |
|---|---|
| Number of classified protein coding genes | 13,983 (90 %) |
| Number of non-classified protein coding genes | 1,535 (10 %) |
Description
This section describes the quality of the predictions and the identification of the predictions coming from the annotation pipeline (see section MAKER prediction). A common problem in de-novo genome annotation is how to measure the quality of the predictions. The MAKER approach includes the Annotation Evidence Distance (AED) calculation. This measures the distance of the prediction to the reference (see section MAKER in chapter Structural gene prediction). So, the smaller the AED is, the more trustful the prediction is (better covered by RNA matching regions). A non-redundant database was used to search for sequence similarity in order to find potential proteins. This database includes over 181 million classified protein sequences. Here we distinguish between three main classes of blast hit situations depending on the coverage of the alignment to the subject (Reference nr protein) and query sequence (P.cal protein) (see Figure 1). Finally, 13,983 proteins showed some similarity to this run (including all three classes from Figure 1), but 1,535 proteins do not share any hit with the nr databse. The unknown proteins were split into two categories by the AED (see figure 2). The unknown proteins with an AED smaller than 0.5 are called "putative uncharacterized proteins" because they have similarities with the reference and have high evidence for having the correct intron/exon strucure but are not characterized. The unknown proteins with an AED above 0.5 are called "hypothetical proteins" because they might not be proteins at all and the evidence of these predictions is low. Finally the functional predictions from relative organisms were compared to P. californicus predictions in order to get an idea of the amount of uncharacterized or unknown proteins from NCBI.Results
Download total functional protein Sequences (13,983 Sequences): [P.cal functional proteins.fa]
Download non-annotated protein Sequences (1,535 Sequences): [P.cal non-annotated proteins.fa]
Download annotation file: [P.cal annotations.gff]
Methods
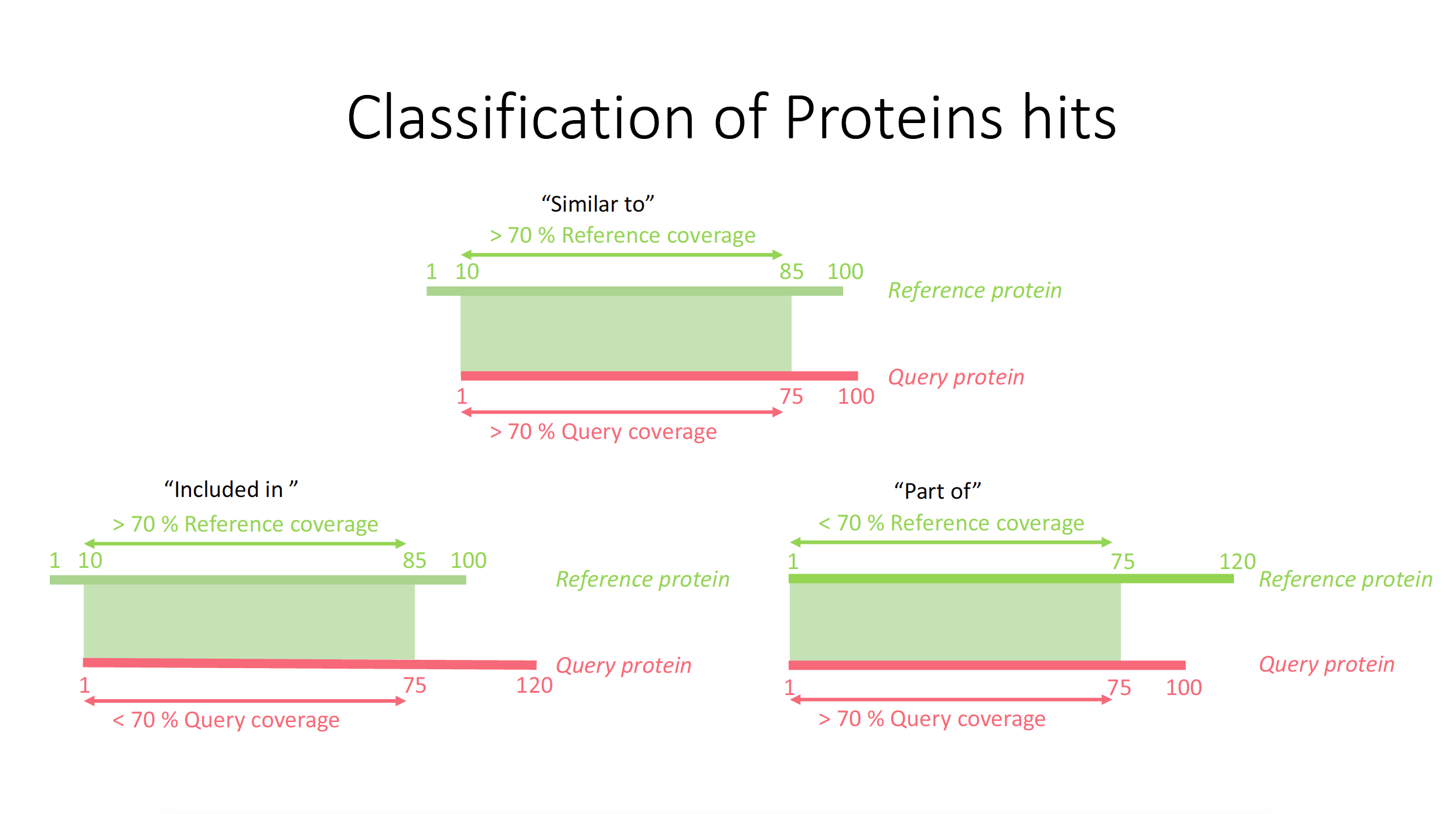
- Figure 2: Cases which can occur during the functional classification of proteins based on BLASTp execution.
ID mapping
Replace IDs with defined prefix IDs:maker_map_ids --prefix Pcal_ --justify 8 P.cal_polished_new_assembly.fasta.all.gff > Pcal_genome.all.id.mapCopy files for renaming:
cp P.cal_polished_new_assembly.fasta.all.gff P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.gff cp P.cal_polished_new_assembly.fasta.all.maker.proteins.fasta P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.proteins.fasta cp P.cal_polished_new_assembly.fasta.all.maker.transcripts.fasta P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.transcripts.fastaMap IDs to gff file:
map_gff_ids Pcal_genome.all.id.map P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.gffMap IDs to fasta files:
map_fasta_ids Pcal_genome.all.id.map P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.proteins.fasta map_fasta_ids Pcal_genome.all.id.map P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.transcripts.fasta
BLAST against uniprot
Build BLAST DB:makeblastdb -in uniprot_sprot.fasta -input_type fasta -title uniprot_sprot.fasta.BLASTDB -dbtype prot -out uniprot_sprot.fasta.BLASTDB -logfile uniprot_sprot.fasta.BLASTDB.logRun BLASTp:
blastp -query P.cal_polished_new_assembly.fasta.all.maker.proteins.fasta -db uniprot_sprot.fasta.BLASTDB -num_threads 10 -evalue 1e-6 -max_hsps 1 -max_target_seqs 1 -outfmt 6 -out output.blastp > blastp.log cp output.blastp output.renamed.blastpMap IDs to BLAST output
map_data_ids Pcal_genome.all.id.map output.renamed.blastp
Domain detection with Interproscan
Run Interproscan:interproscan.sh -i P.cal_polished_new_assembly.fasta.all.maker.proteins.fasta -cpu 10 -o output.iprscan -appl pfam -dp -f TSV -goterms -iprlookup -pa -t p > interproscan.log cp output.iprscan output.renamed.iprscanMap IDs to Interproscan output:
map_data_ids Pcal_genome.all.id.map output.renamed.iprscan
Mapping functional detection to gff and fasta
Map functional detections from BLAST to gff and fasta:maker_functional_gff Pogonomyrmex_Refseq.fasta output.renamed.blastp P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.gff > Pcal.renamed.putative_function.gff maker_functional_fasta Pogonomyrmex_Refseq.fasta output.renamed.blastp P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.proteins.fasta > Pcal.maker.proteins.renamed.putative_function.fasta maker_functional_fasta Pogonomyrmex_Refseq.fasta output.renamed.blastp P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.transcripts.fasta > Pcal.maker.transcripts.renamed.putative_function.fastaAdd Domain predictions:
ipr_update_gff Pcal.renamed.putative_function.gff output.renamed.iprscan > Pcal.renamed.putative_function.domain_added.gff iprscan2gff3 output.renamed.iprscan P.cal_polished_new_assembly.renamed.all.gff > visible_iprscan_domains.gff
2020-11-18 22:05