Summary
Results of the homolgy-based genome annotation for P. californicus.| Target genome | Reference genome | Number of predicted genes |
|---|---|---|
| P. californicus | A. melliferra | 711 |
| P. californicus | C. floridanus | 2,207 |
| P. californicus | S. invicta | 3,151 |
| P. californicus | P. barbatus | 8,944 |
| P. californicus | Summary of unique predictions from A. melliferra, C. floridanus, S. invicta, and P. barbatus | 15,013 |
Description
The GeneModelMapper (GeMoMa) iis an annotation pipeline used to find protein coding genes while using the genome of an already annotated relative species as a reference, genome. First it extracts protein-coding exons from well-annotated reference genomes (see Figure 1). After this, individual exons are matched to locations on the target genome by tblastn. GeMoMa tries to match the resulting models from a tblastn run to the genome by using additional RNA sequences from the target species. The resulting model of this step can have a huge variance depending on the quality and completeness of the reference species. Four different species (A. melliferra, C.floridanus, S. invicta, and P. barbatus) which are relative to P. californicus (see Overview) were used as reference genomes (see Table in Results). The final step includes the merging of the different runs by using different reference genomes and filtering them with a final annotation filter. Finally, all resulting annotations are filtered for identical duplicated genes.
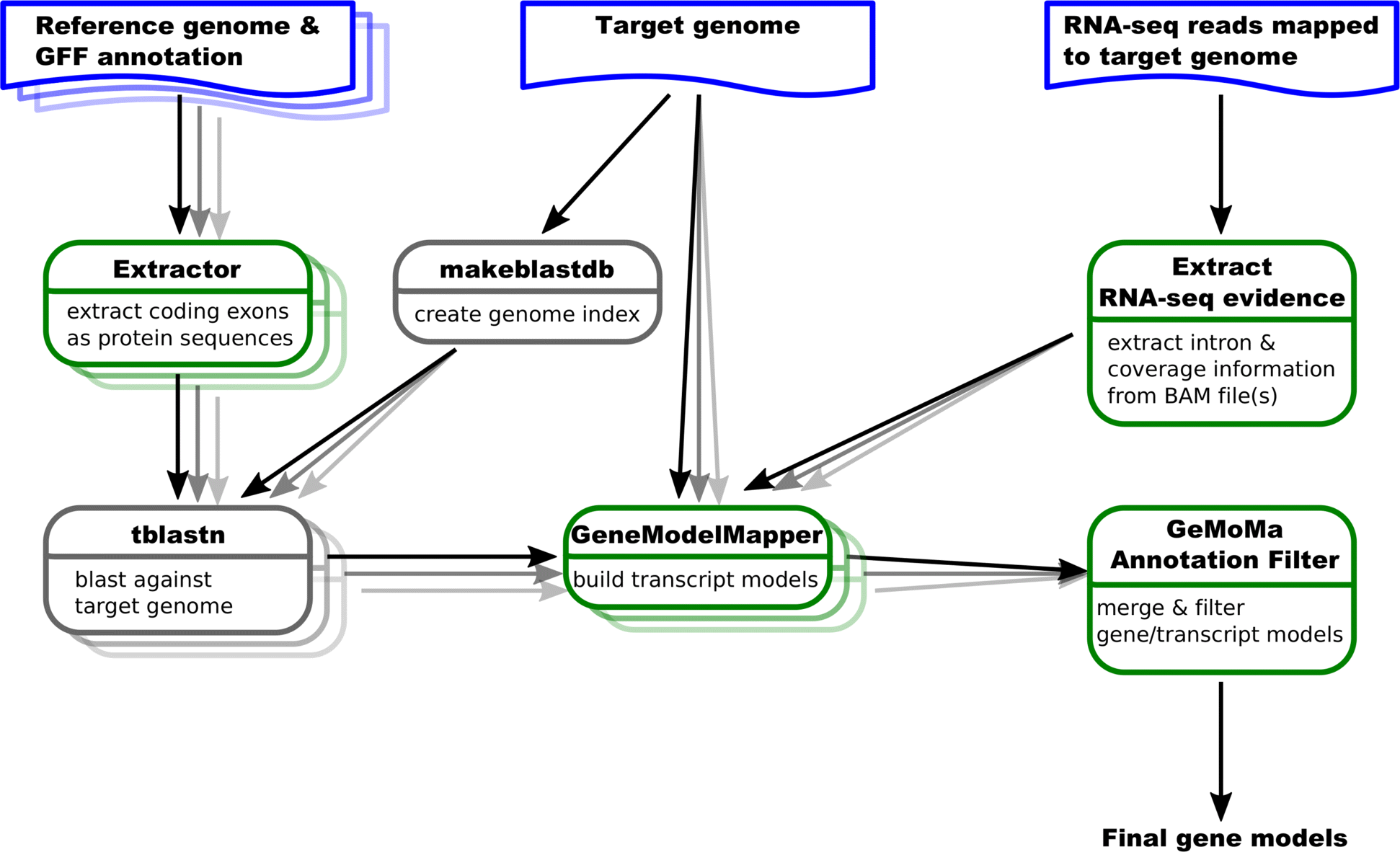
- Figure 1: Overview of the algorithm from the GeMoMa pipeline. Blue items represent input data sets, green boxes represent GeMoMa modules, while grey boxes represent external modules.[Source: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw092 ]
Results
The final GeMoMa gene prediction is based on species which are relatives on different levels. The most relative species to P. californicus is P. barbatus, then S. invicta, and the least is C.floridanus. The smaller the pylogenetic distance of the species is to P. californicus, the more the predictions are based on them as a reference organism.
Download GeMoMa annotation: GeMoMa_annotation.gff
Download Protein sequences: GeMoMa_proteins.fasta
Download Transcript annotation: GeMoMa_transcript.fasta
References
- Jens Keilwagen, Michael Wenk, Jessica L. Erickson, Martin H. Schattat, Jan Grau, Frank Hartung; Using intron position conservation for homology-based gene prediction, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 44, Issue 9, 19 May 2016, Pages e89 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw092
- Jens Keilwagen, Frank Hartung, Michael Paulini ,SvenO.Twardziok and Jan Grau Combining RNA-seq data andhomology-based gene prediction for plants,animals and fungi, BMC Bioinformatics, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2203-5