Summary
Summary of predictions from the MAKER pipeline.| Prediction | Number of sequences |
|---|---|
| Proteins | 15,688 |
| unique Proteins | 15,160 |
| Transcripts | 15,688 |
| unique Transcripts | 15,518 |
Description
MAKER 2 is a genome annotation pipeline for smaller eukaryotic and prokaryotic genomes. The MAKER algorithm uses different prediction programs (see figure 1) for mask repetitive elements in the genome (RepeatMasker), aligns proteins and RNA evidence to the genome assembly (BLAST), includes data from relatives, and identifies splice sites (Exonerate). The repeat annotation step was skipped because it was performed earlier with a custom designed repeat database (see Repeat masking section ). MAKER makes use of gene prediction software, Augustus and Semi-HMM-based Nucleic Acid Parser (SNAP), as gene finders. Augusts predicts genes in eukaryotic genomic sequences by using the Generalized Hidden Markov Model (GHMM) to align Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) and proteins to the genome. SNAP deals with Hidden Markoc Models (HMMs), as does Augustus, but this program uses these models to calculate similarities of intron length probabilities. Additionally, MAKER uses tRNAscan ffor detection of tRNA. The Annotation Edit Distance (AED) was developed (Eilbeck et al., 2009; Holt and Yandell, 2011; Yandell and Ence, 2012) to measure the evidence of the annotations coming from MAKER. The AED is a number between 0 and 1, where 0 means the entire gene is covered by RNA matching regions. MAKER can be trained by itself and by other programs like Augustus or SNAP. The data from GeMoMa as well as the data from relatives were handed to the pipeline (see figure 2). For the first run of MAKER, the Nasonia reference model for Augustus detection was used. Resulting MAKER predictions from the previous run with an AED smaller that 0.25 were handed to SNAP for generating more accurate gene models to train MAKER in the next round. This was done in order to provide a reduction of false positive protein predictions. The third MAKER round was done by using a BUSCO trained Augusts reference model based on single copy ortholgous genes from Hymenoptera clades in the P. califonicus assembly. The GHMM from the Augustus training were used to train MAKER in the fourth and last round.

- Figure 1: MAKER algorithm description. The RepeatMasker step was skipped, because it was performed earlier with a customized repeat database. Gene finders are used as Augusts and SNAP [Source: http://www.yandell-lab.org/publications/pdf/maker_current_protocols.pdf].
Results
Description: Ending of the protein ID (with RB, RC, RD etc.) refers to the isoforms of the protein coding gene. MRNA in the gff file refers to the gene and its region in the genome.
Transcripts
Download unique transcripts fasta from (15,518 sequences): P.cal transcript sequences.fasta
Proteins
Download proteins according to unique transcripts (15,518 sequences): P.cal protein sequences.fasta
Annotation
Download structural annotation of unique transcripts gff: P.cal final predictions.gff
Discussion
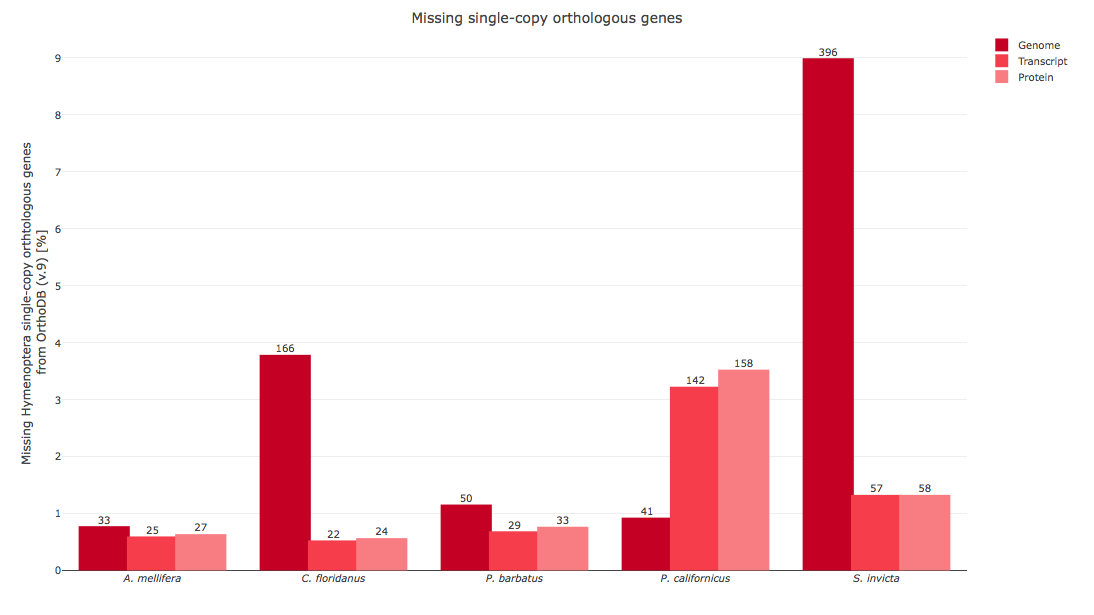
- Figure 2: Comparison of Annotation completeness between relative species.
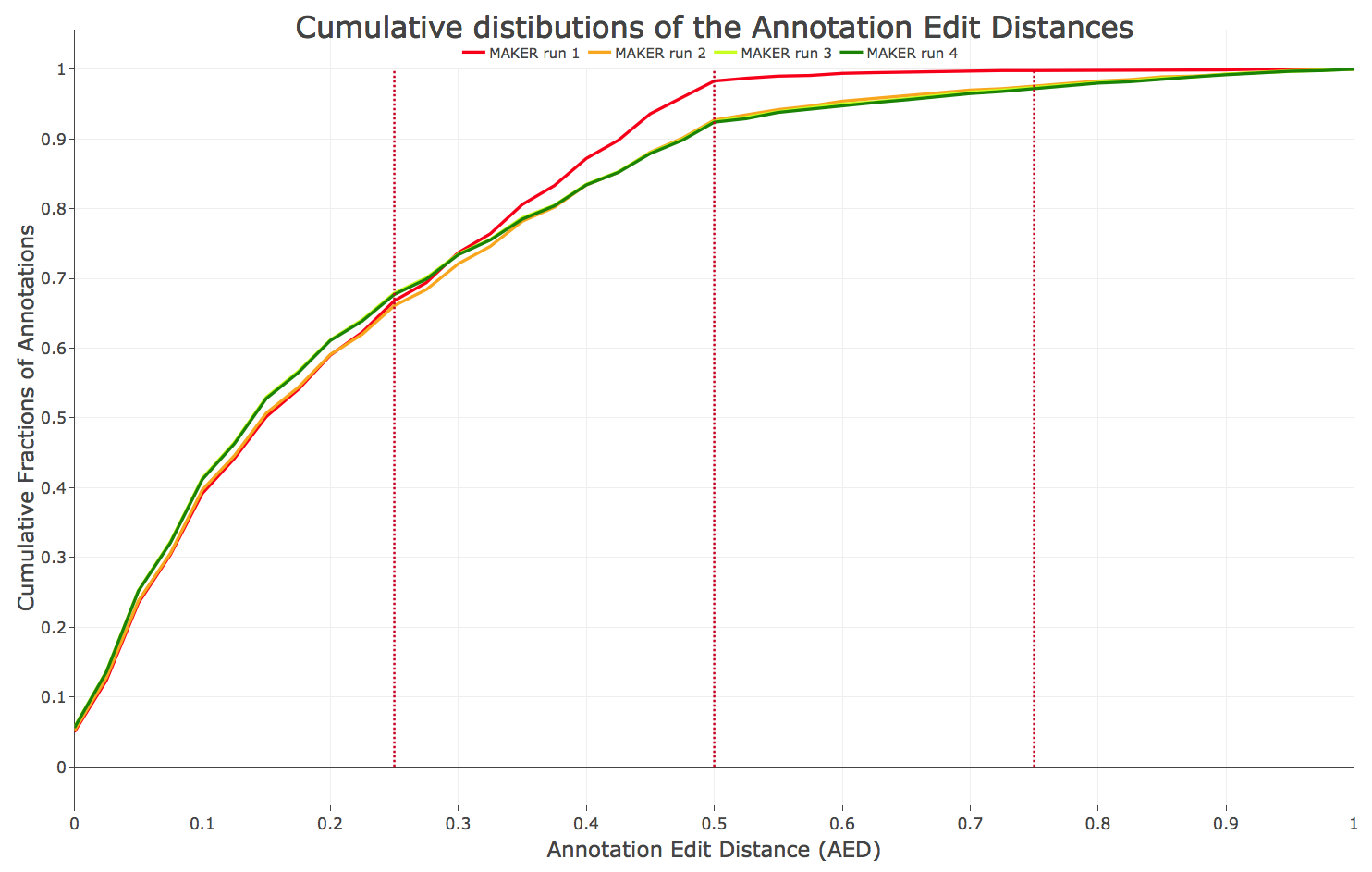
- Figure 3: Annotation Edit Distances (AED) of all performed MAKER rounds (within MAKER training). An increasing accuracy during the training is noticeable (more annotations covered by RNA data with lower AED).
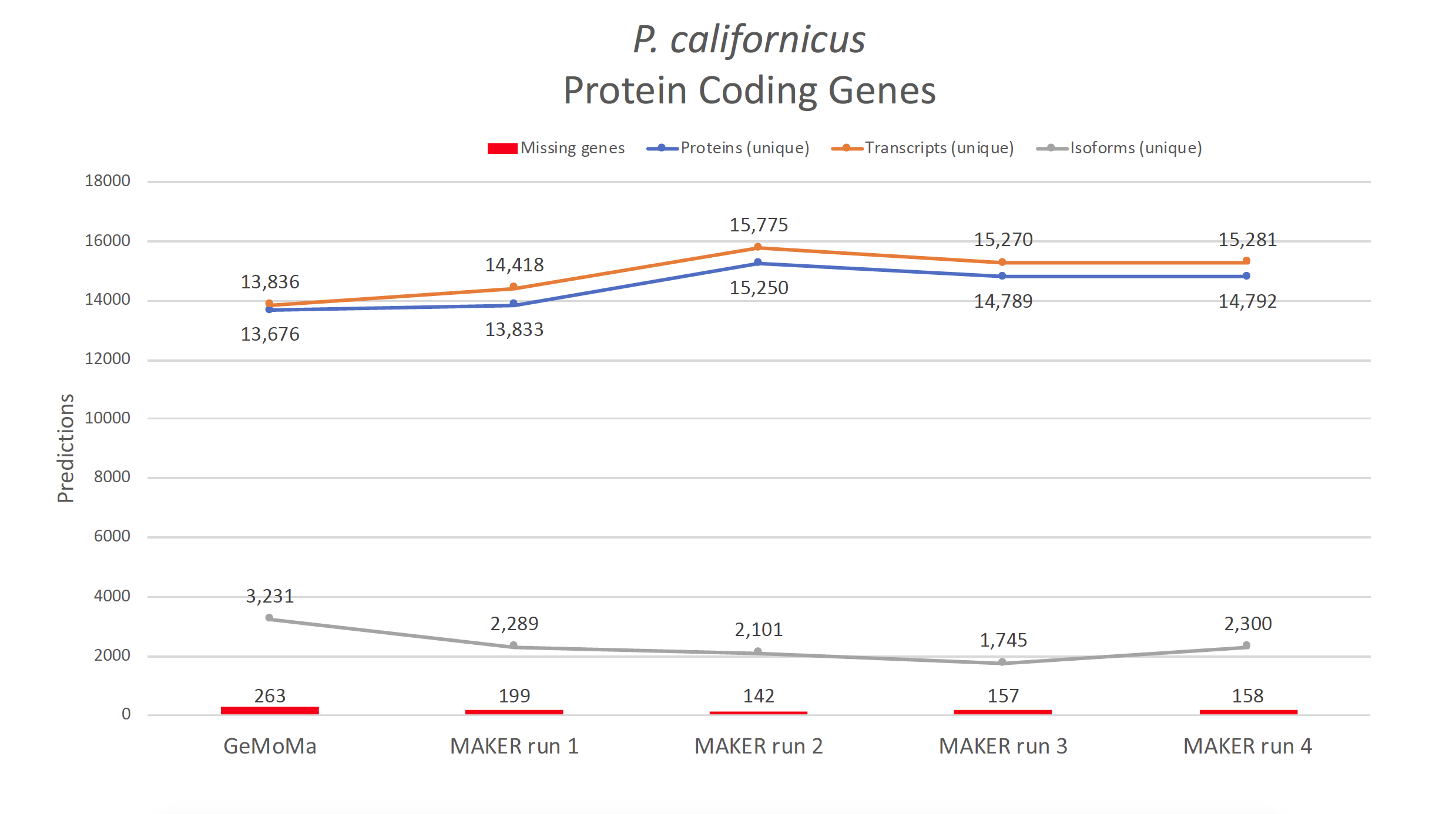
- Figure 4: Summary of predictions between annotation pipeline GeMoMa and MAKER. Changes of annotation numbers during MAKER training.
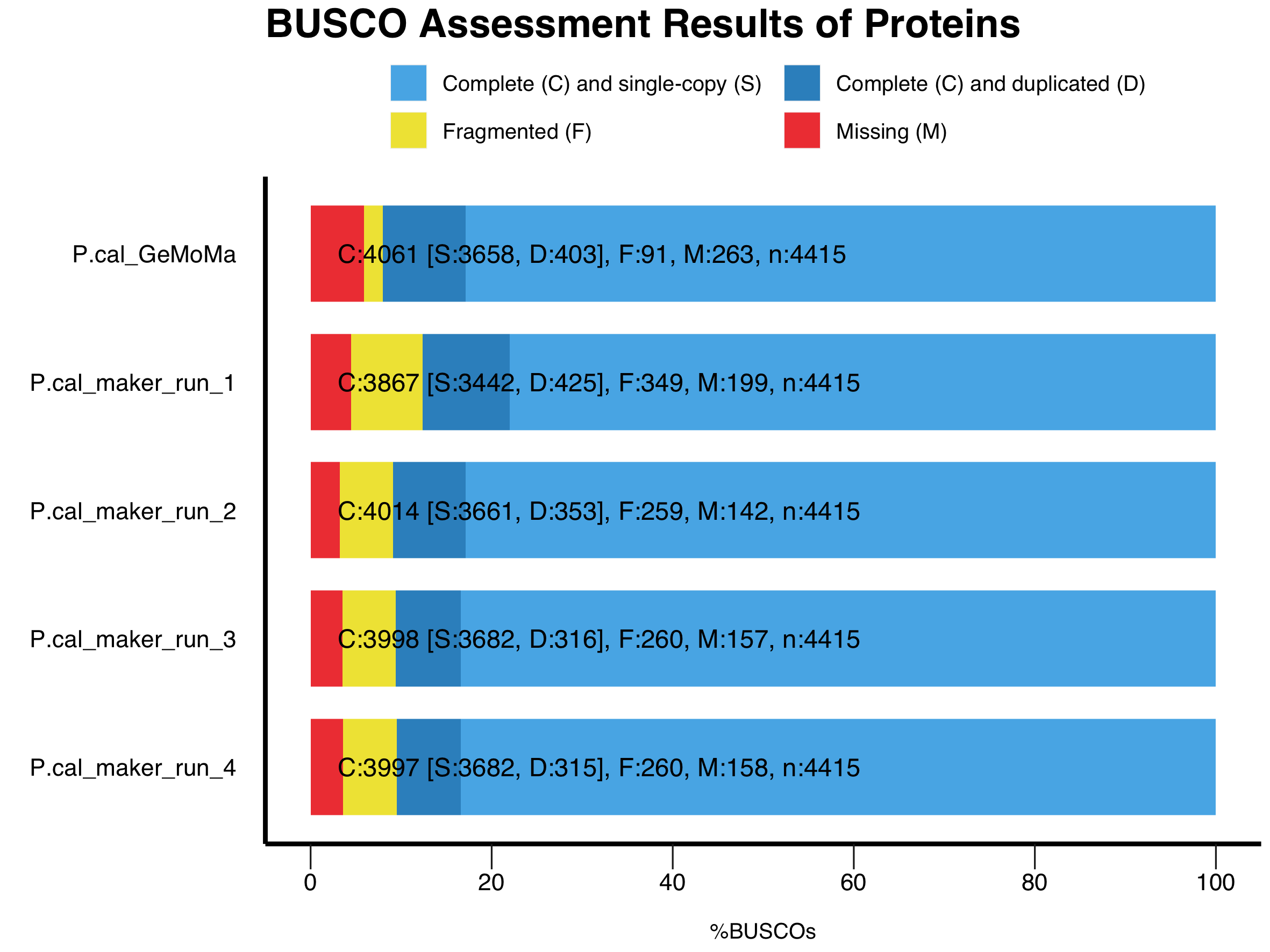
- Figure 5: Protein annotation completeness comparison based on BUSCO results between Pipelines (GeMoMa vs MAKER) and within MAKER training.
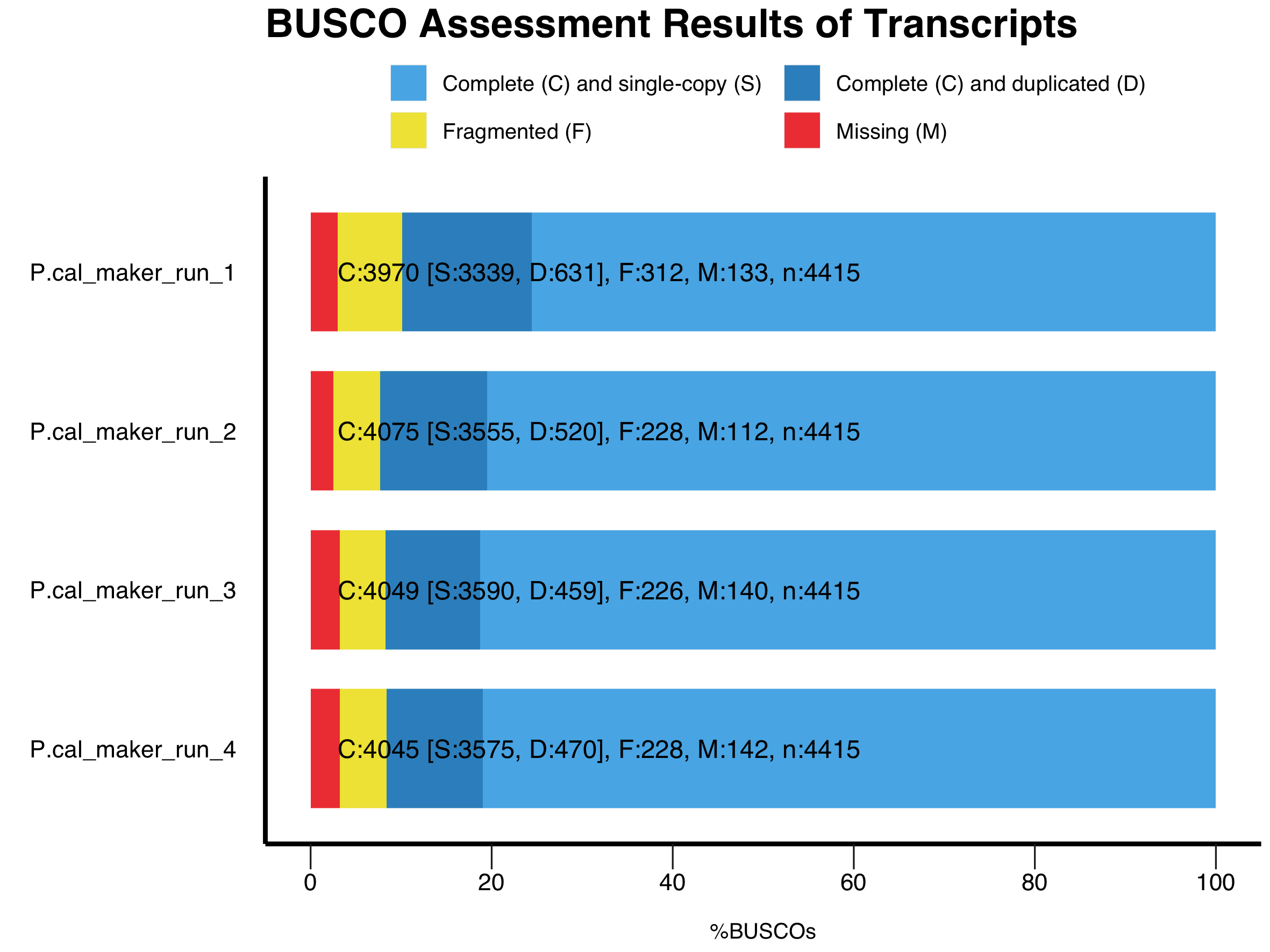
- Figure 6: Transcripts annotation completeness comparison based on BUSCO results between Pipelines (GeMoMa vs MAKER) and within MAKER training.